A study published recently in the American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology confirms that shiitake mushroom extract can inhibit liver fibrosis. The research indicates that AHCC acts in two ways, which may be key in preventing cirrhosis and cancer of the liver organ.
Lentinula edodes, more widely known as shiitake, is a species of fungus that has been used in the cuisine and medicine of East Asian countries for thousands of years.
Studies have confirmed its anti-cancer properties, its ability to lower cholesterol, and its protective effect on the liver.
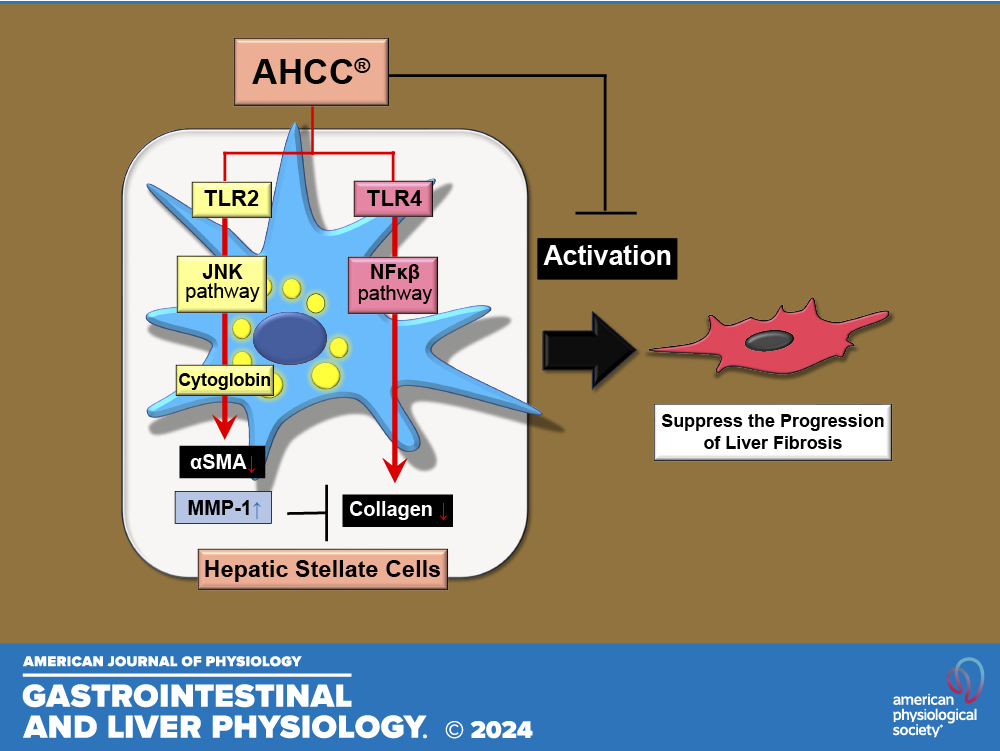
Dr. Hayato Urushima’s team from the Graduate School of Medicine at Osaka Metropolitan University studied how AHCC (a standardized extract of cultured Lentinula edodes mushroom), protects the liver. Experiments were conducted on mice to test the effect of AHCC on liver fibrosis. The results indicate two pathways of action of the extract:
- Reduction of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
Mediated by Toll-like receptor protein (TLR2), AHCC induces cytoglobin, a protein that reduces the level of reactive oxygen species. Excess ROS is one of the main factors causing liver damage.
2. Suppression of collagen expression
The second mechanism of action of AHCC is to block the expression of collagen through the TLR4 channel. As a result, the process of liver fibrosis is inhibited, significantly reducing the risk of cirrhosis.
As indicated by the results of mouse studies, AHCC appears to act on two pathways that lead to inhibition of liver fibrosis, which may prevent cirrhosis of this organ.
Source: www.journals.physiology.org