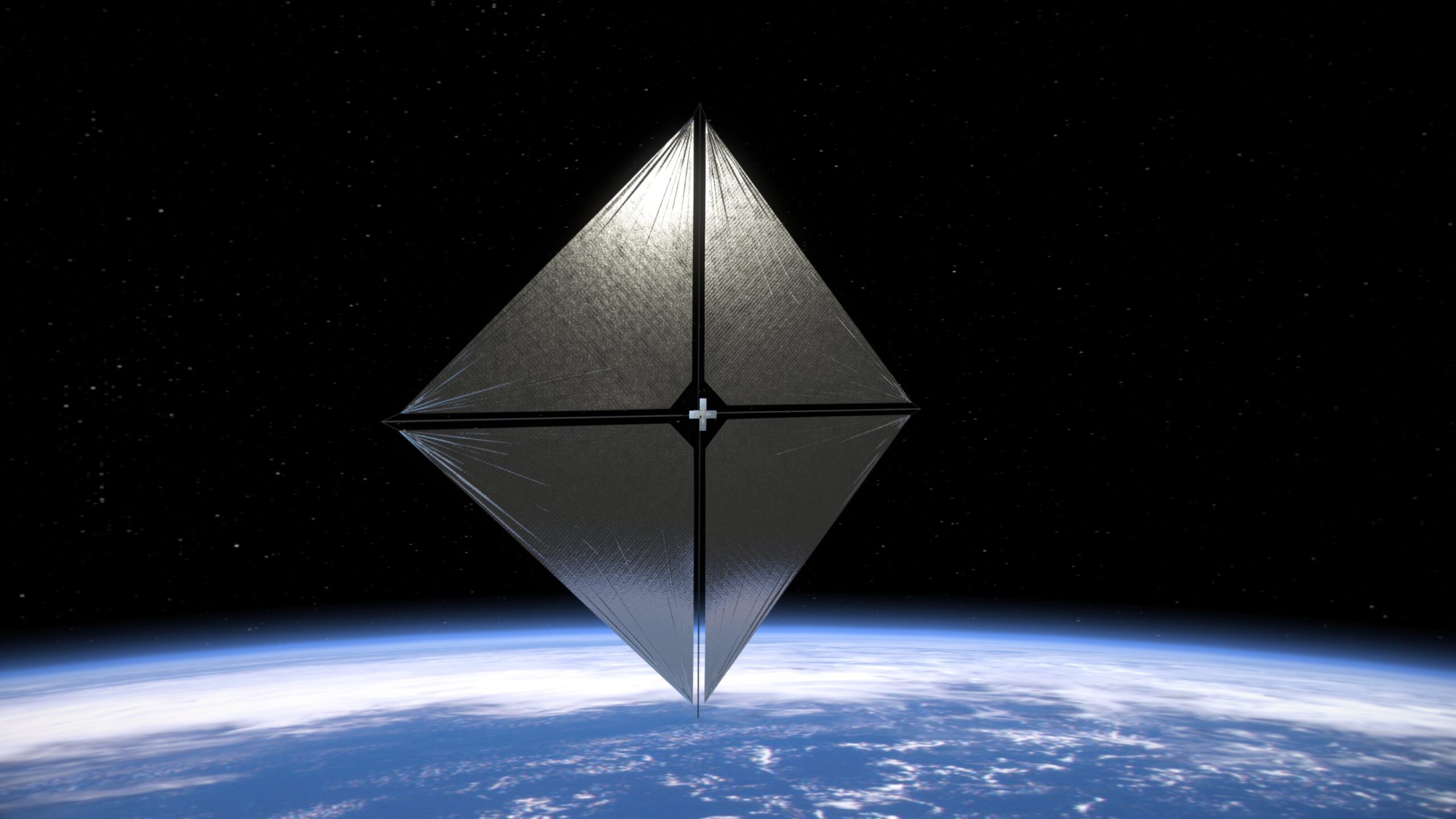
The US space agency NASA is testing a solar sail in Earth’s orbit. The 80-meter-square structure has already been unfurled and is visible from the surface of the globe. Scientists stress that the space sail opens up new possibilities in the exploration of the universe.
How does the solar sail work?
The solar sail works by reflecting photons – particles of sunlight – which transfer their kinetic energy to the to the sail (i.e., they exert pressure on it, which propels the object). Although the force generated by the photons is small, in space, where there is no air resistance, it allows the object to reach significant speeds over long periods of time. Researchers believe that solar sails could advance space travel in the future by allowing spacecraft to travel great distances without the need for carrying heavy fuels.
The NASA solar sail measures about 80 square meters and operates at an altitude of more than 1,000 kilometers. Thanks to its large size, it can be seen from Earth. According to nocneniebo.pl, it can also be observed from Poland. Its flight begins in the southern sky and ends in the north.
The future of space travel
According to Rocket Lab, the company that delivered the Electron rocket (on which the sail was launched into orbit on April 24), the success of the mission could have a significant impact on the future of space exploration. It has been pointed out that the success of ACS3 (Advanced Composite Solar Sail System) ACS3 paves the way for the use of solar sails in future interplanetary and even interstellar missions.